Complementary (alternative) medicine: everything there is to know!
Published Aug 5, 2023 • By Candice Salomé
The terms complementary and alternative medicine (CAM), and integrative healthcare are used to designate practices that can be used in addition to so-called conventional, or mainstream, healthcare, with the aim of contributing to patients' well-being. Massage, chiropractic, hypnosis, mesotherapy, auriculotherapy, acupuncture... There are many types of non-conventional medicine, and it can be difficult to find one's way around them and choose what is best for patients in different situations.
So what can we use unconventional medicine for? For whom can it be recommended? Is it covered by health insurance?
We explain it all in our article!
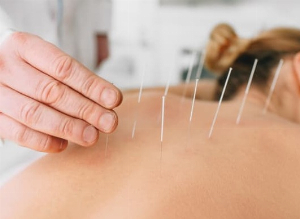
What is complementary and alternative medicine?
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is unconventional, non-mainstream therapy. It encompasses several hundred different therapeutic practices. The World Health Organization (WHO) lists over 400 of them.
Their effectiveness has only recently become the subject of scientific studies or recognized clinical trials, unlike so-called conventional practices, whose effectiveness has long been established.
The WHO (World Health Organization) distinguishes between four types of alternative medicine:
- Biological therapies, which use natural products derived from plants, minerals or animals, such as phytotherapy and aromatherapy,
- Manual therapies such as massages, chiropractic and reflexology,
- Mind-body approaches such as medical hypnosis, meditation and sophrology,
- Systems based on their own theoretical foundations, such as acupuncture or homeopathy.
Unconventional treatments that do not require the use of drugs or chemical molecules. In this sense, they are distinguished from allopathic (traditional) medicine by the treatments they offer, often based on manipulation and the use of natural products.
What can we use complementary and alternative medicine for?
Conventional medicine focuses more on the consequences of illness than on its causes. The logic behind it is the following: if there is a problem, solve it; if there is an illness, treat it. Conventional medicine focuses on the symptoms it is trying to treat. Following a precise diagnosis, a treatment is prescribed, the dosage of which is regulated and adjusted depending on the situation.
Conventional and unconventional medicine are therefore both separate and complementary.
These two forms of medicine offer a global approach to treating health conditions. Conventional medicine establishes a diagnosis, based on science, whereas unconventional medicine tends to place the patient in a holistic context (the environment, nature, energy, etc.). Symptoms are then treated in their entirety: causes and consequences. It is therefore important to never turn away from traditional medicine to the detriment of alternative medicine.
Alternative approach covers a wide range of conditions. It can treat headaches, stress, anxiety, phobias, stomach aches, allergies, skin problems, back pain, addiction, insomnia, etc.
Nevertheless, proving the efficacy of these unconventional treatments remains a complicated task. For medical science, it is more difficult to evaluate a complementary medicine than a conventional drug. Drugs are industrial products and they all contain the same molecules, whereas two hypnotherapists, for example, will not work with hypnosis in the same way.
How can you add alternative medicine to your treatment plan?
Although the effectiveness of some complementary therapies has yet to be proven, others are recognized by the public health authorities and are quite popular.
Acupuncture is useful for patients suffering from chronic pain such as migraine, osteoarthritis, neck pain, etc. Acupuncture has also been shown to be beneficial for patients suffering from vomiting and nausea after chemotherapy or surgery. When acupuncture is integrated into an overall treatment process, it can be rather effective.
Similarly, osteopathy sessions after surgery can help patients get back into shape more quickly, especially if the operation involves the back or the intestines.
Hypnosis is proving highly effective for managing pain and stress, and for avoiding general anesthesia during surface operations. The term "hypnoanalgesia" is used to replace anesthesia, "hypnosedation" can be a solution to reduce stress and pain during invasive medical examinations or childbirth. Hypnosis is also increasingly used in medicine and psychotherapy to treat addictions, phobias, depression, etc.
In all cases, unconventional medicine should be used with caution.
Is complementary and alternative medicine covered by health insurance?
The use of complementary and alternative medicine in the United States is regulated by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. The term "alternative medicine" is often being dropped now if favor of "integrative" healthcare. The center is supervising research in the field of complementary medicine and provides guidance for physicians, patients, practitioners and regulators.
If you want to try unconventional medicine, you should check with your healthcare insurance provider, to see if they cover this type of therapy, and to what extent. Some plans cover unconventional treatment provided that the practitioner is also a licensed physician, others may deny coverage if they consider the practice as unsafe and "experimental".
Even though out-of-pocket costs of complementary medicine can be significant, according to statistics, more and more Americans turn to this type of medicine (total visits to CAM practitioners exceed total visits to all primary care physicians), making it a profitable business. Therefore you should always inquire into the unconventional practice you'd like to try, and make sure the CAM practitioner has all the necessary qualifications and/or is a licensed healthcare provider.
Was this article helpful to you?
Give it a "Like" and share your thoughts and questions with the community in the comments below!
Take care!
Sources :
"Médecines" non conventionnelles, Economie.Gouv
Médecine non conventionnelle, Wikipédia
De quoi les médecines complémentaires et alternatives sont-elles le nom ?, France Assos Santé
Les médecines douces sont-elles réellement efficaces ?, Essentiel Santé Magazine
Médecines complémentaires : comment s’y retrouver ?, Essentiel Santé Magazine
Le boom des médecines douces, Entreprendre
Assurance santé médecine douce : remboursement des pratiques naturelles, Cocoon
1 comment
You will also like
What are the dangers associated with the over-the-counter sale of certain medicines?
Dec 19, 2020 • 6 comments

 Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter