Contraception methods: benefits and risks of different contraceptives
Published Jul 11, 2023 • By Polina Kochetkova
Contraception methods are important for many reasons: they can protect you from unwanted pregnancy and save you from a lot of stress. However, with more than 12 different contraceptives out there, it can be difficult to find the right one for you. Today we discuss the benefits and side effects of every contraceptive method.
Keep reading to find out!
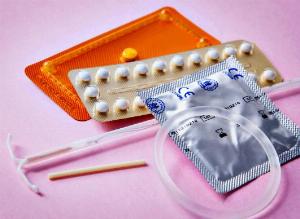
What is called birth control?
The use of techniques or tools to avoid unintended pregnancy is known as birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control. Although birth control has been practiced since antiquity, modern times saw the development of reliable conception control methods.
Finding the most suitable contraceptive method is crucial for both single people and couples trying to avoid pregnancy. It can be confusing to navigate through the advantages and disadvantages of each approach to contraception with so many options available.
Many types of contraceptives, including barrier techniques, hormonal methods, and long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), can be used, however, it is important to know about the benefits and disadvantages of each one. In order to choose the best type of contraception for your unique circumstances and medical background, it is crucial to speak with your doctor.
What are the types of contraception?
Barrier methods
Fertilization-blocking techniques create a physical barrier to block sperm from contact with the egg. Condoms for men and women, the diaphragm, the cervical cap, and the contraceptive sponge are a few examples. These techniques have several advantages, including accessibility, and the absence of negative hormonal side effects. To achieve effectiveness, they must be used correctly and consistently. The few possible negative effects are typically caused by allergies or sensitivity to latex. Only condoms offer STI protection.
Short-action hormonal contraceptives
The birth control pill, vaginal ring, skin patch, and contraceptive injection are examples of short-acting hormonal therapies that need to be administered on a regular basis. When used properly, these techniques offer dependable contraception as well as extra advantages including regulated menstrual cycles and less menstrual pain. However, they could result in negative side effects like nausea, sore breasts, mood swings, or irregular bleeding. Daily, weekly, or monthly administration must be followed for maximum effectiveness.
Some contraceptives work by using hormones comparable to those produced naturally by women such as estrogens and progestins.
Some women, especially those with medical issues like breast cancer, shouldn't use contraceptives that include these hormones.
Long-action hormonal contraceptives
Long-acting hormonal approaches, that include the contraceptive implant (Nexplanon), the hormonal intrauterine device (Mirena), and copper intrauterine devices (ParaGard, Skyla, and Kyleena), among others, give extended contraception without requiring daily monitoring. These techniques provide long-lasting safety, convenience, and great efficiency. Hormonal treatments, however, could result in negative side effects such as headaches, mood swings, or irregular bleeding. Minor surgical procedures are needed for placement or removal.
Sterilization
For people or couples who no longer want to have children, permanent sterilization treatments, such as tubal ligation for women and vasectomy for men, offer a long-term alternative. Although highly effective, these operations must be considered permanent. Potential hazards include painful recovery after surgery, complications from the procedure, and in rare cases, ectopic pregnancy. It's crucial to understand that sterilization does not offer STI defense.
Emergency contraception
Emergency contraception (Plan B pill) is not intended as a replacement for standard birth control. But if you engage in unprotected intercourse and your method of birth control is ineffective, it is an alternative. Emergency contraception must be administered as soon as possible following unprotected sex in order to be successful.
What are the natural contraceptive methods?
Fertility awareness
Fertility awareness methods (FAMs) are strategies to keep track of your menstrual cycle and fertile days so you can avoid getting pregnant. Other names for FAMs include "natural family planning" and "the rhythm method."
With fertility awareness techniques, you may keep track of your menstrual cycle and learn when your ovaries produce an egg each month. Ovulation is the term for such a time of the month.
Your fertile days—the times when you're most likely to become pregnant—occur close to ovulation. On such "unsafe," fertile days, people use FAMs to avoid becoming pregnant by avoiding sex or utilizing another method of birth control (like condoms).
Withdrawal
By blocking semen from the vagina, withdrawal, also known as pulling out, prevents pregnancy. When combined with other birth control methods, such as a condom, withdrawal works best.
Pulling out is exactly what it sounds like - removing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation. You can become pregnant if semen enters your vagina. Therefore, it is preventative to ejaculate away from a vulva or vagina. But for this to work, you must be sure to pull out every time you have vaginal intercourse before any semen comes out.
Breastfeeding
Lactational amenorrhea technique (LAM) is another name for breastfeeding as a birth control strategy.
Your body stops ovulating when you exclusively breastfeed your baby, which requires that you nurse at least every four hours during the day and every six hours at night. If you don't ovulate, you can't become pregnant.
LAM isn't a great birth control strategy if you are breastfeeding but also use formula. If you feed your child something other than breast milk, breastfeeding won't prevent pregnancy. Another aspect to keep in mind is that in order to use breastfeeding as birth control you should not use breast pump.
Keep in mind that breastfeeding only functions as a birth control method for the first six months of a baby's life or until your period resumes.
Overall
It's important to consider each person's needs, preferences, and potential negative effects while selecting the best contraceptive.
Barrier techniques offer simple accessibility and no hormonal side effects, yet might not fit individuals with allergies to materials the contraceptives are made from, for example, latex.
The ease of short-acting hormone treatments comes at the cost of regular administration. Negative side effects notably headaches, nausea, painful breasts, and vaginal yeast infections (thrush) are examples of possible drawbacks. Additionally, the hormones may result in mood swings, spotting in between periods, and a decrease in a woman's sexual desire.
Extended contraception is possible with long-acting hormonal treatments and simple surgical procedures. Although it offers a long-lasting remedy, permanent sterilization should be viewed as irreversible.
To receive individualized advice and to talk about any worries or particular medical conditions, it is essential to seek the advice of a healthcare professional. Keep in mind that contraception has health benefits beyond pregnancy prevention.
Give it a "Like" and share your thoughts and questions with the community in the comments below!
Take care!
Comments
You will also like
What are the dangers associated with the over-the-counter sale of certain medicines?
Dec 19, 2020 • 6 comments

 Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter